By default IIS 7 will generate a new session when accessing a site over a secure HTTPS connection. This can cause issues if you are switching between a HTTP and a HTTPS connection when dealing with a site that handles logged in users via sessions.
Luckily this is a easy fix.
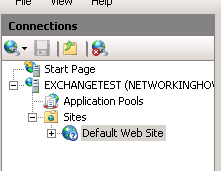
Open up the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, and select the web site you wish to change the setting on:
Open up the “ASP” feature:

Expand the “Session Properties” section:
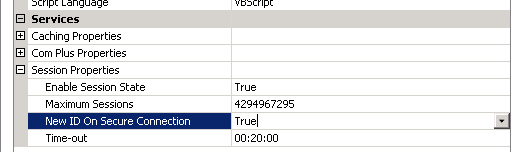
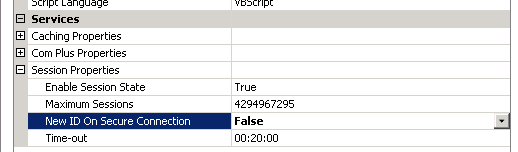
Change the drop down option for “New ID ON Secure Connection” from “True” to “False”.
Restart the web site to make sure the settings take effect.
This guide shows you how to restart a specific IIS 7 web site from the command line. This can come in very handy if you need to automate restarting the site.
IIS 7 includes a command line management tool called “appcmd.exe” which allows you do do a wide range of tasks, including stopping and starting specific websites.
The “appcmd.exe” program isn’t in the ‘PATH’ environment variable, so you must run it from within the correct folder, or add the folder to your PATH environment variable.
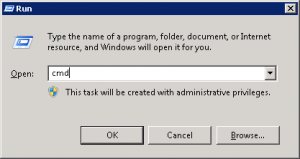
Open a command window by clicking the start button, and typing cmd.exe into the search and hitting enter.
(or by pressing the WINDOWS KEY + r combination on the keyboard, and typing cmd.exe”, and clicking “OK”)
Change to the C drive, or whatever drive your OS/Windows folder is installed on:
C:
Change directory to the location where appcmd.exe resides (c:\windows\system32\inetsrv\):
cd %WINDIR%\system32\inetsrv
Issue the following command to view the web sites available on the server:
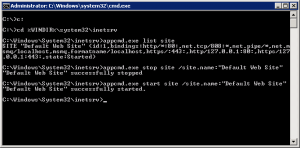
appcmd.exe list site
You should get something like the following returned on the screen:
SITE "Default Web Site" (id:1,bindings:http/*:80:,net.tcp/808:*,net.pipe/*,net.m smq/localhost,msmq.formatname/localhost,https/:443:,http/127.0.0.1:80:,https/127 .0.0.1:443:,state:Started)
The main part of this we need to take note of is the site name, which in this case is “Default Web Site”.
Run the following command to stop the specified website, using the above site name to reference what site you want to stop:
appcmd.exe stop site /site.name:"Default Web Site"
To start the site back up, run the following command:
appcmd.exe start site /site.name:"Default Web Site"
The web site should now be started again.
The whole process should look like this:
Note: You can always reference the appcmd.exe file directly, instead of changing directories first, using the following path:
%WINDIR%\system32\inetsrv\appcmd.exe
A default installation of IIS 6 on a Windows machine (Server or workstation) will limit the maximum request size for ASP scripts to 200kb. This may not cause any issues for most users, however when you start to integrate file uploads and similar functions, you may find that you encounter this issue. A common ASP error that occurs when the limit is set too low is “‘ASP 0104 : 80004005’ Operation not Allowed”. Luckily this limit is easy to change, and will be outlined in detail below.
This issue is cased by the “AspMaxRequestEntityAllowed” setting in the IIS metabase, which is stored in the “C:\Windows\System32\Inetsrv\MetaBase.xml” file. Please make sure you take a backup of this file before making any changes. Preferably take the backup after the web service has stopped, so you can be sure no other applications have the file currently open.
The first thing that needs to be done, is to stop the IIS Web server.
Click the “Start” button.
![]()
Browse to “Administrative Tools”.
Select the “Services” item.
The “Services” window should now appear. From here you can start and stop services that are set up on the machine.
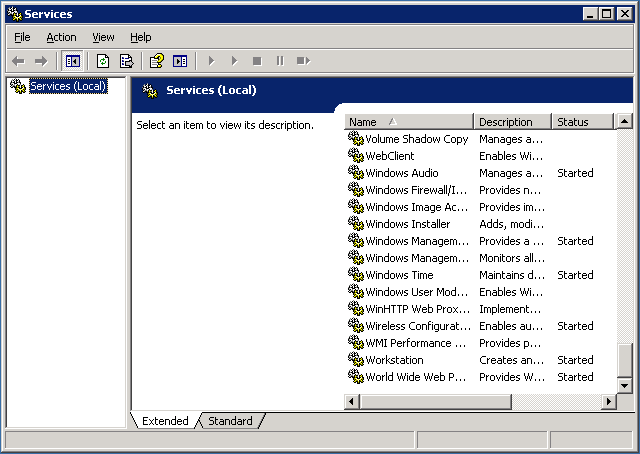
Scroll all the way down to the bottom, and highlight the “World Wide Web Publishing Service” service.
Right click on the “World Wide Web Publishing Service” service, and select “Stop”.
The service will now stop. Depending on how many sites you have set up in IIS, the time it takes for this to stop may vary. It shouldn’t take too long.
Once the service has been stopped, you can modify the Metabase.xml file. This file contains all the IIS settings.
Open notepad, or your favorite text file editor, and select to open a file.
Type in, or browse to the following file:
c:\windows\system32\inetsrv\MetaBase.xml
If you choose to browse, you may find that you wont see the file, unless you change the “Files of type” option to “All Files (*.*’).
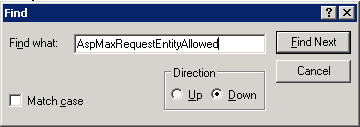
Use the find tool in Notepad, and search for the first occurance of:
AspMaxRequestEntityAllowed
You should find an entry like this:
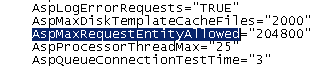
The “204800” option at the end of this line is the limit in bytes.
eg. 204800 / 1024 = 200kb
You need to change this value to whatever you need it to be. For this example I will set it to 2mb, as I don’t need it to be set too high.
2 x 1024 x 1024 = 2097152 bytes
You can use the above calculation, substituting the 2 for how many megabytes you wish to set the value to.
Update the value in Notepad to reflect your required size limit.
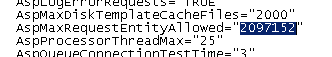
Save the file, and exit out of the text editor.
Go back to the services window from before. If you closed it, reopen it.
Right click on the “World Wide Web Publishing Service” service again, and click “Start”.
The service should now appear as “Started”.
![]()
If the service hasn’t started for some reason, check the Windows Event viewer.
Make sure you take a backup of the Metabase.xml file via windows explorer first before making any changes. Editing this file incorrectly will cause IIS not to start, so care should be taken with any modifications to this file.

